Introduction to Kadaknath
The poor farmers, not having animal husbandry with his agriculture occupation, are committing suicide. Because they are not able to payback the loans. This more so even true where the agriculture is dependent on rains and if there is a drought then the population of that area has no option other than migrating to cities. They cannot migrate to
In Indian villages where there is a green revolution and agriculture is possible, they are dependent on Holstein cows and good Buffalo’s. In the arid zone where agriculture is poor, they are dependent on sheep, goat, mule, and camel. In these areas, they are traditionally not inclined towards the poultry keeping. They are mostly vegetarian or if they eat meat, they eat goat meat. In the villages where agriculture is dependent on rains, there are a certain class of peoples maintain local hen in small number. For their Money requirement, they sell the birds. They may also eat birds.
Keeping the exotic birds for livelihood as a broiler or laying is not possible. It is because they cannot afford feeding cost of birds and these exotic birds suffer from detrimental diseases, so all of the birds may die overnight. However, the cost of egg and meat sold from exotic birds, exotic broiler birds is not profitable.
It is for the above reason that Kadaknath bird which is resistant to diseases, and can thrive on local grains and insects in the wild, is getting popular because its egg and meat has medicinal value, its meat is black it is high in iron content and other nutrients which are good for Asthma, tuberculosis, migraine and increasing sexual potential in mens.
It is for this season that its eggs are sold for 50 rupees each, meat is sold for 500 to 800 rupees per kg. So one Kadaknath bird producing one egg is equal to 10 eggs of the exotic layer birds, and so is true for its meat. Now the
The Kadaknath bird does not hatch the eggs, so the eggs are hatched in incubator. And baby chicks are brooded and distributed to the farmers, these birds does not need protection from disease, they can survive on poor nutrition, and they do not need elaborate housing. If farmer is maintaining 50-100 birds, then he can earn his livelihood. This will help in stopping migration from drought areas to big cities in search of earning money.
We are giving the success story of a farmer under Mhow (M.P) veterinary college which is given below.
SUCCESS STORY OF A POULTRY FARMER
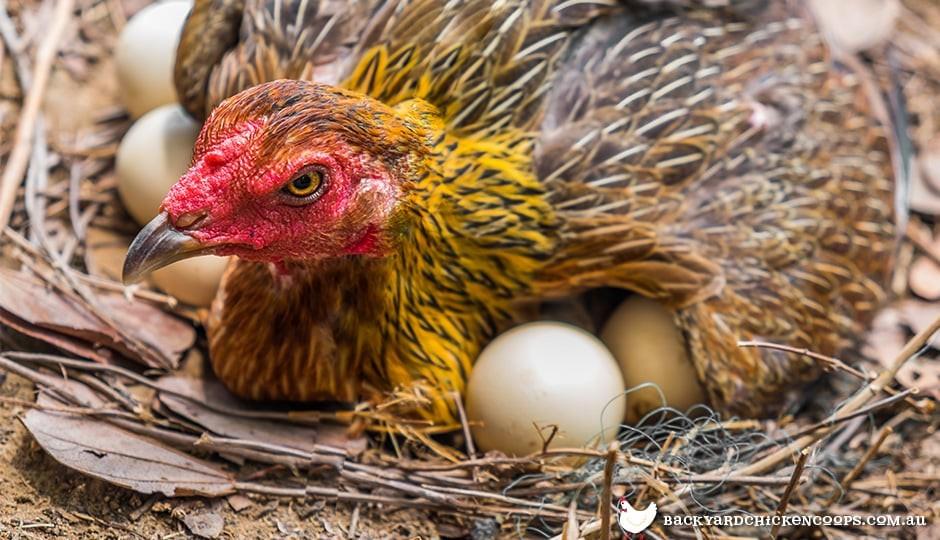
The fertile eggs and chicks of Kadaknath birds are being sold to the poultry farmers for conservation and multiplication of the Kadaknath breed of poultry reared under the project entitled “Conservation and scientific evaluation of Kadaknath breed of fowl”.
One of the poultry farmer Mr Raju, Village Betma, District Indore, M.P., use to rear Desi birds and Broilers in his farm. Mr Raju came to know through his friends that fertile eggs and Kadaknath birds are being sold at College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, Mhow. He purchased approximately 100 fertile eggs and about 100 chicks/growers/adult birds from Veterinary College, Mhow.
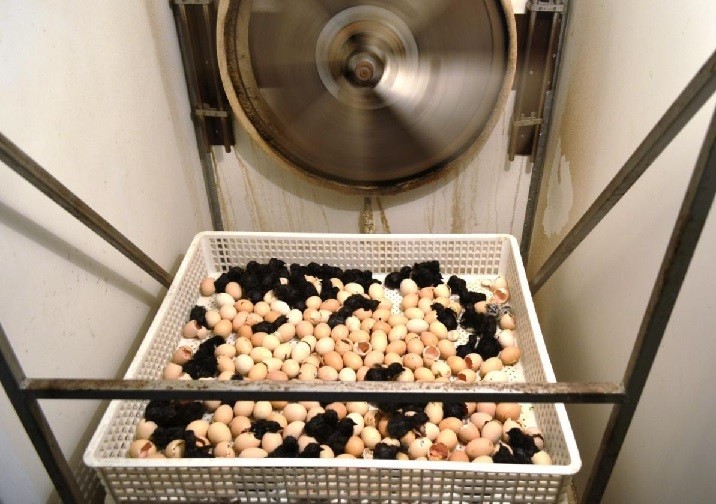

Technical know how for scientific rearing of birds was extended to the farmer from time to time. Various processes involved in hatchery were also shown to him. Mr Raju very carefully observed the temperature, humidity and turning of the eggs carried out in the hatchery. After reaching his farm in the village Betma, Mr Raju indigenously prepared a wooden box. With the help of an electric bulb and a water bowl, he provided the required temperature and humidity to the fertile eggs for hatching. The farmer got 65 % hatchability at his farm, which was a huge success. Now he is a regular customer of Kadaknath fertile eggs and birds. He is earning a handsome amount through the sale of Kadaknath birds. He has become an example for other farmers of the State.
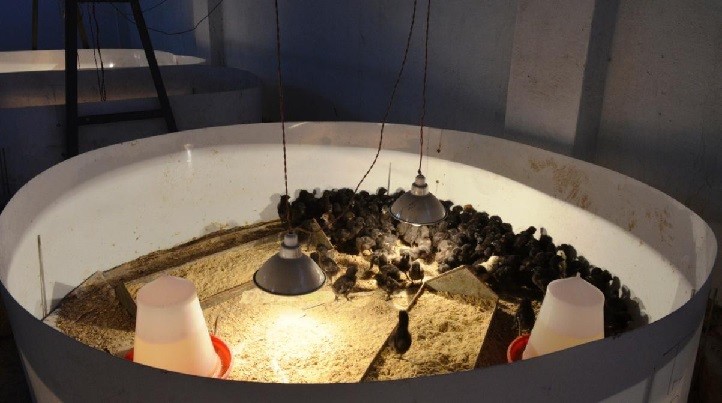

The Madhya Pradesh government recently launched a mobile app for Kadaknath, named “MP Kadaknath”. This app claims to connect with poultries that sales Kadaknath to the peoples, other parts of states and country. They said that the app will provide
Hatching and Brooding
How to use a incubator to hatch eggs
The incubator is an artificial method for hatching of the eggs, it allows you to hatch eggs of a hen in controlled conditions in large numbers. Its working principle is the same as the natural hatching.
Cleaning of the incubator is the first step to avoid diseases. This can be done before and after every batch of hatching.
Placing of the incubator also an important, use an incubator at 25-28°C and humidity of 50%. You should calibrate the temperature of the incubator before placing eggs in it. The temperature should be between 37-38°C (99-102°Fahrenheit). The humidity of the incubator needs to be adjusted which should be around 40-50%.
Identify the fertile eggs, the age of eggs should be 7-10 days, older eggs will not hatch. Record the period of the incubation. Chicken eggs usually take 21 days to hatch. Keep rotating the trays in the incubator, in some incubator there are automatic rota-tor. You should expect 55-75% of the eggs to hatch.
Stop rotating the eggs 3 days prior to the estimated hatch date (usually 21 days). Humidity level to be increased now, it should be around 60%. Leave the incubator closed even if the chicks are hatched, open the incubator once the chicks are three days old. It’s important to keep the chicks in the incubator until they are completely dry. You may have to decrease 1-2 degree of the temperature of the incubator once the eggs are hatched and chicks are there.
Brooding of Chicks
Brooding is the process of rearing chicks. It can be done naturally or artificially.
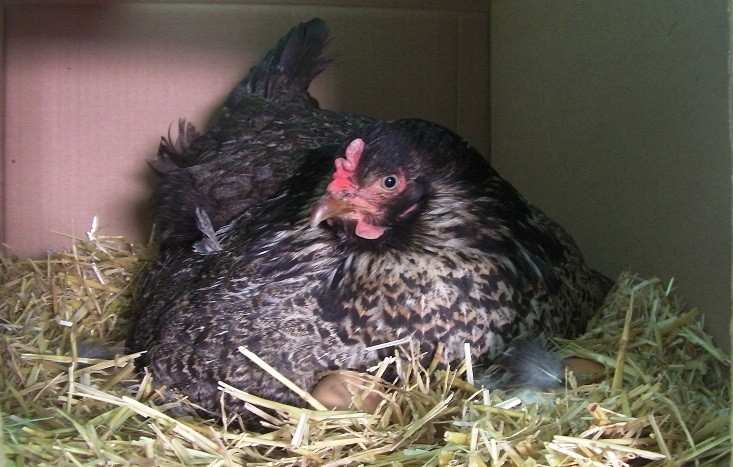
Natural process of brooding is done by the hen itself for 2-3 weeks after hatching.


Artificial brooding is used when the chicks are in a larger number. It raises chicks the same as they are raised naturally by providing favourable conditions, and temperature.
Here is a list of some steps of brooding:
Floor brooding
This is the process of brooding chicks on the floor, and this method is widely used by growers because the need for the material will be less.
Flooring
For floor material, absorbent materials are used which can absorb the water or waste materials. Litter can be used for making the floor, it should not be slippery, a slippery surface can cause many problems to the chicks.
Ideal litter for flooring are sawdust, chopped straw or wood shavings etc.
Litter must be changed within time to time or replaced if it gets wet or dirty. When chicks are 4-5 weeks old, litter should be changed more frequently.
Brooder guard/chicks shield
For surrounding the brooder, cardboard sheets and wire sheets can be used. The side of the brooder guard works as the chick shield. It keeps them away from reaching to other birds. The guard shield can be removed after some time.
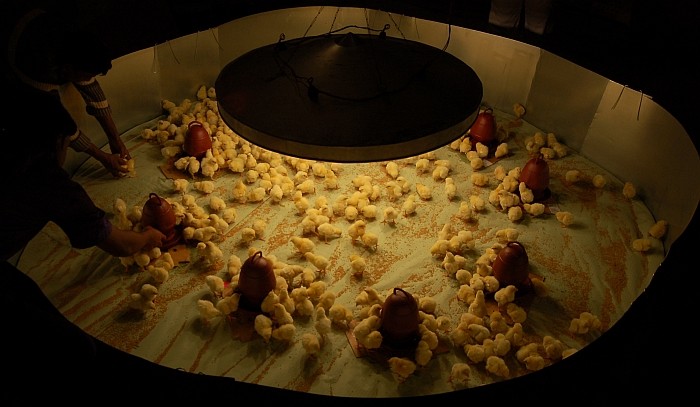

Heat
When dealing with a small number of chicks, heat is given by lamps, or electric bulbs are used. But when chicks are more than 250 in the brooder you can use heating equipment. The temperature must be maintained, chicks are cold-blooded during the first week of hatching, and they are unable to maintain their body temperature when the age increases the warmth of the blood also increases.
Starting temperature for the chicks is 35°C or 95°F, and drop 5°F temperature every week when it becomes similar to the environmental conditions, or until chicks grow feathers.
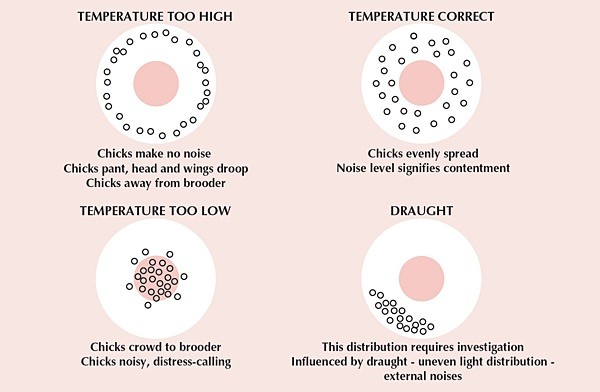
Effect of heat can be seen in the chicks behavior if the environment is too cold chicks will be near to the heat source, if it’s too warm for them they will get away from the heat source. If they are roaming around it, the temperature is normal. See the picture below to understand it correctly.
Lighting
Light plays an important role in brooding. On starting the light is provided 24 hours a day. After some time i.e. 7-8 weeks light should be given 16 hours. When chicks are of 10-20 weeks they should be placed on short day period, 6-7 hours of light.
Floor space
Chicks need space to grow up, when they are newborn freshly hatched they are short, but they can grow more rapidly, by 6 weeks they can get a decent weight and size.
Water space and feeder space
Water should be placed in a distance of 1-2 feet of length, where chicks can easily eat or drink water.
Feeding of the Chicks
Diet of the chicks should be a balanced diet. Starter of the chicks should contain all the necessary nutrients. Supplements should not given in starting
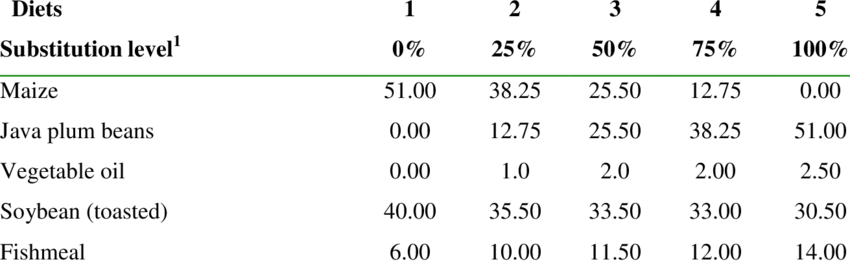
Baby chicks do not need starch, heavy supplements of starch will reduce the nutrients intake and it will result in poor growth of chicks. After the age of 6 weeks, they can be fed a grower diet. The adult diet should not be given to the baby chicks, especially layer diets because it contains a lot of calcium. Water must be provided constantly. Feed chart is given below.
Once the chicks are mature you can feed them the normal diet, or homemade feed. You can also give them hydroponic fodder and berseem etc (more details are given in next heading).
How to reduce the cost of feeding
Feeding can be reduced by growing your own maize, berseem,
Maize
This is best crop for cows. It can be grown in black and red soil. The pH of the soil should be 5.8 to 8.0 one hectare area needs 60 kg seeds. It gives 35 kg nitrogen and 40 kg P2O3 at flowering. The distance between lines should be 20 to 30 cm.

Maize 
Maize
It can be grown from February to April (60 days) and April -June and full-time August. You can harvest all crops in one day and take up the next sowing. You can harvest 300 quintal this depends on rainfall, irrigation and crop management. In summers (February to June) you can take the second crop. So, you can make 600 quintal silage from February to July.
Hydroponic Fodder
In this process from one kg grains, you can harvest eight kg of fodder in 8 days. What you need is water, pH and continuous supply of light and trays. No fertilizer or soil is needed.
The pH should be 6.0 to 6.5 humility by 60 to 65 and temp 20° to 25°C temperature and humility is critical the temperature and humidity restrict the growth. First, you soul the 20 kg seed of bajra wheal or burly for 12 hours. To restrict the growth of fungus, add DOMAX in water it will be easily available in the market.


After 24 hours take out seed and keep then wrap in cloth for 24 hours at a warm place. You need a tray with a hole in the bottom of the size of 2×3 feet and 3 inch high. Spread seeds in keeping tray and light as shown in picture provide water by sprinkler contentiously. The fodder will come up in 8 days.
Berseem

This is a fast-growing winter crop in northern India. This crop is sown in October and harvested after 60 days. It gives a yield of 300 to 400 quintal per Acer. It needs 8 -10 kg seeds per
Feeding worms to the chickens
Most of the peoples ask a question that can we feed red worms (mealworms) to the chicken? The answer is Yes! We can.
Red worms are not only good composting worms, but they can also be used as a protein-rich, nutrient-packed animal food i.e. chicken food.
If you grow them your own, you can save more money in feeding your poultry, it is very cost effective. But only cons is there it takes a bit time to be grown, but the wait is worth. You can also sell the worms, if you have grown them in enough amount., and can make more money from them.

Vaccination of chickens
This vaccination scheme can be applied to all poultry chicken breeds.
| Diseases | Age and booster dose | Route |
| Ranikhet disease | 1-7 Days 3-4 Weeks 8 Weeks 16-18 Weeks | spray/ occulonasal drops/drinking water spray/drinking water i/m or s/c Drinking water i/m |
| Marek’s disease | 1 Day | i/m |
| Infectious bursal disease | 40th Week | Drinking water |
| Infectious bronchitis | 3 Weeks | Drinking water |
| Infectious coryza | 3 Weeks | Drinking water |
| EDS – 76 | 3 Weeks | Drinking water/spray |
| ILT | 3 Weeks | i/m |
Diseases in chicken
Marek’s disease

Fowl Pox disease
Ranikhet disease
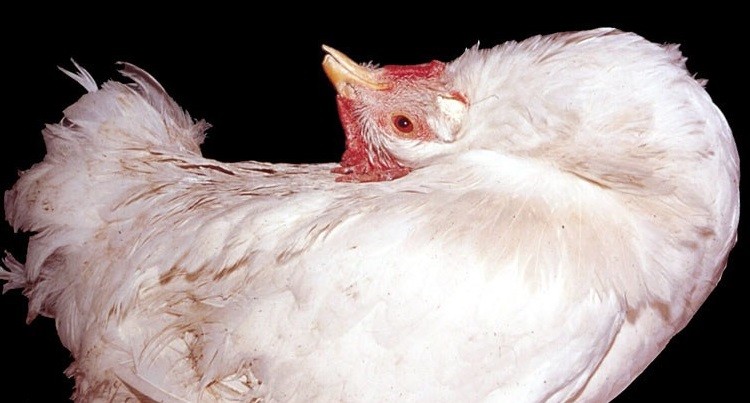

How egg is formed in a hen?
Egg formation occurs in the reproductive tract of the chicken, or we can say hen. The reproductive tract can be divided into two parts.
Ovary
Oviduct
The Ovary is where the yolk is added and when it reaches the right size it is released from the ovary through a process called ovulation. The infundibulum then picks up the released yolk and passes it to the magnum, where the albumin is added and passed further to the isthmus for the addition of the shell membranes. The developing stage of an egg is completed in the shell gland. In the shell gland, the shell of the egg and shell pigments are then added to it. After going through the formation process when the egg is assembled, it travels to the oviduct. In the last, it is pushed out from the vagina.
Source: Youtube
Albumen It is the clear part of the egg, also known as the egg white. When it gets cooked it becomes white hence named egg white. Two layers of albumins are present on an egg one is near to the yolk and the second a thin layer.
Yolk The yellow part present in the centre of the egg.
Chalaza It is located in the albumen, it is simple albumin and keeps the yolk to the centre of the egg.
Shell membranes Cell is covered by two membranes one is called inner membrane and second is called the outer membrane.
Shell It is the outermost part of an egg, gives protection to the inner components.
What is clutch period?
The laying bird consumes 100 gm of feed and produces an egg in 26 hours. Hence after giving 2,3,4,5, there will be a day gap. And 1,2,4,5, is known as clutch size. In exotic laying birds, the bird gives 250 eggs per year. So after laying 4-5 eggs, there is a gap of one day. In Kadaknath it gives only 150 eggs, so after 2-3 days there will be a gap.
How to know that bird is giving egg or not?
At the economical aperture there are two pelvic bones on each
What is broodiness?
Desi bird in the month of March April they become broods, that means they don’t give eggs, and they have the urge to sit and hatch the eggs. If they find some egg on the ground when they hatch the chicks from these eggs. For hatching of the eggs, the room temperature should not be above 25°C.
Guineafowl
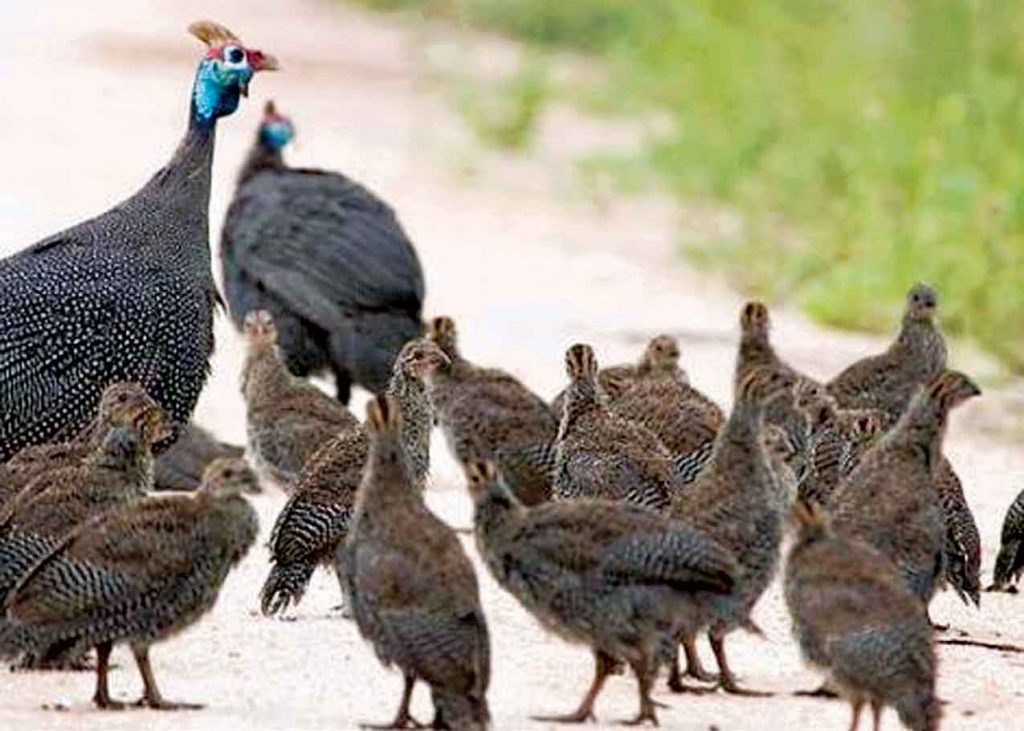

For control of the rats, snake, and humongous you can keep 10 Guineafowl per 100 K
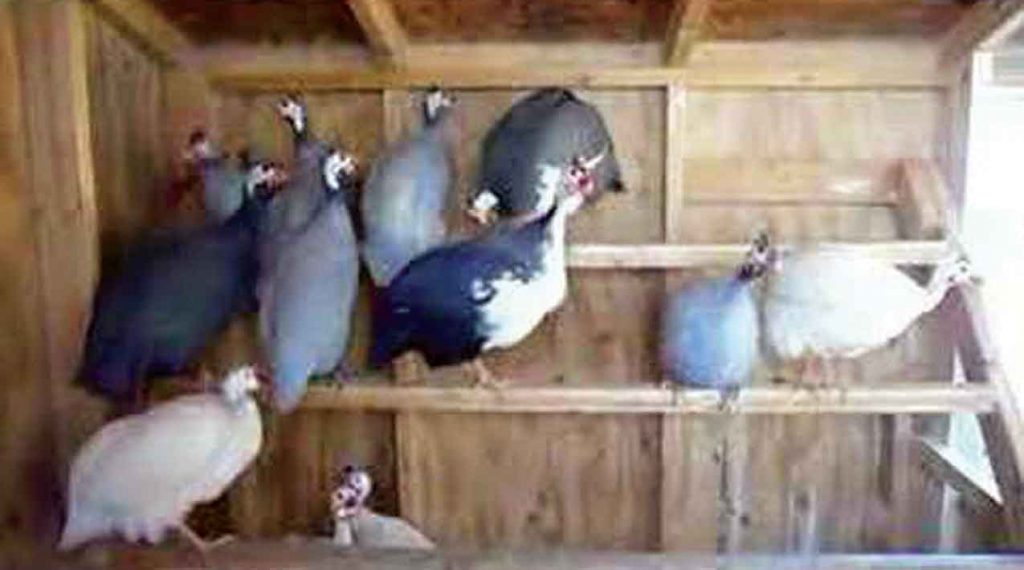


So guineafowl grazers, the grass is their food. In the poultry house at night, they sit at a height. They lay eggs in summers. They lay 10-15 eggs then they brood them. Its chick comes out from the egg after 30 days. In an incubator, you can incubate them at 95°F. These birds are not good mothers. Their chicks are given, poultry starter for 6 weeks then they survive on insects and grass, they save the poultry feed from pests and white ants. They fly a long distance in the flock and come back to their home.

